| bin | ||
| build | ||
| resources | ||
| samples | ||
| src | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| build.sh | ||
| install.vala.in | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| meson.build | ||
| README.md | ||
| valadoc.sh | ||
pluie-yaml
pluie-yaml is a vala shared library managing yaml files (v 1.2) and yaml nodes in vala language.
As json is now a valid subset of yaml, you can use this lib to load json files too.
The purpose of this project is to make vala able to load and deal with yaml configuration files.
So, currently the lib deal only with one yaml document (it's not recommended to use multiples doc),
but you can use a special ^imports clause (special mapping node) to load a subset of yaml files
in the main yaml document.
The lib partially manage tag directives and tag values (basic types and Yaml.Object extended objects types).
with version 0.5, pluie-yaml is now able to :
- parse yaml file with vala tags => transform to Yaml.Node
- Build Yaml.Object from Yaml.Node (with some glue for struct and non Yaml.Object derived types)
- Build Yaml.Node from Yaml.Object (with some glue for struct and non Yaml.Object derived types)
pluie-yaml use the (License MIT, many thanks to Kirill Simonov) to parse and retriew related yaml events.
License
GNU GPL v3
Prerequisites
valac meson ninja libyaml glib gobject gmodule gee pluie-echo
see https://git.pluie.org/pluie/libpluie-echo in order to install pluie-echo-0.2 pkg
Install
git clone the project then cd to project directory and do :
meson --prefix=/usr ./ build
sudo ninja install -C build
Compilation
valac --pkg pluie-echo-0.2 --pkg pluie-yaml-0.4 main.vala
You can use ./build.sh to rebuild/install the pluie-yaml lib and compile samples files
Api / Documentation
https://pluie.org/pluie-yaml-0.5/index.htm
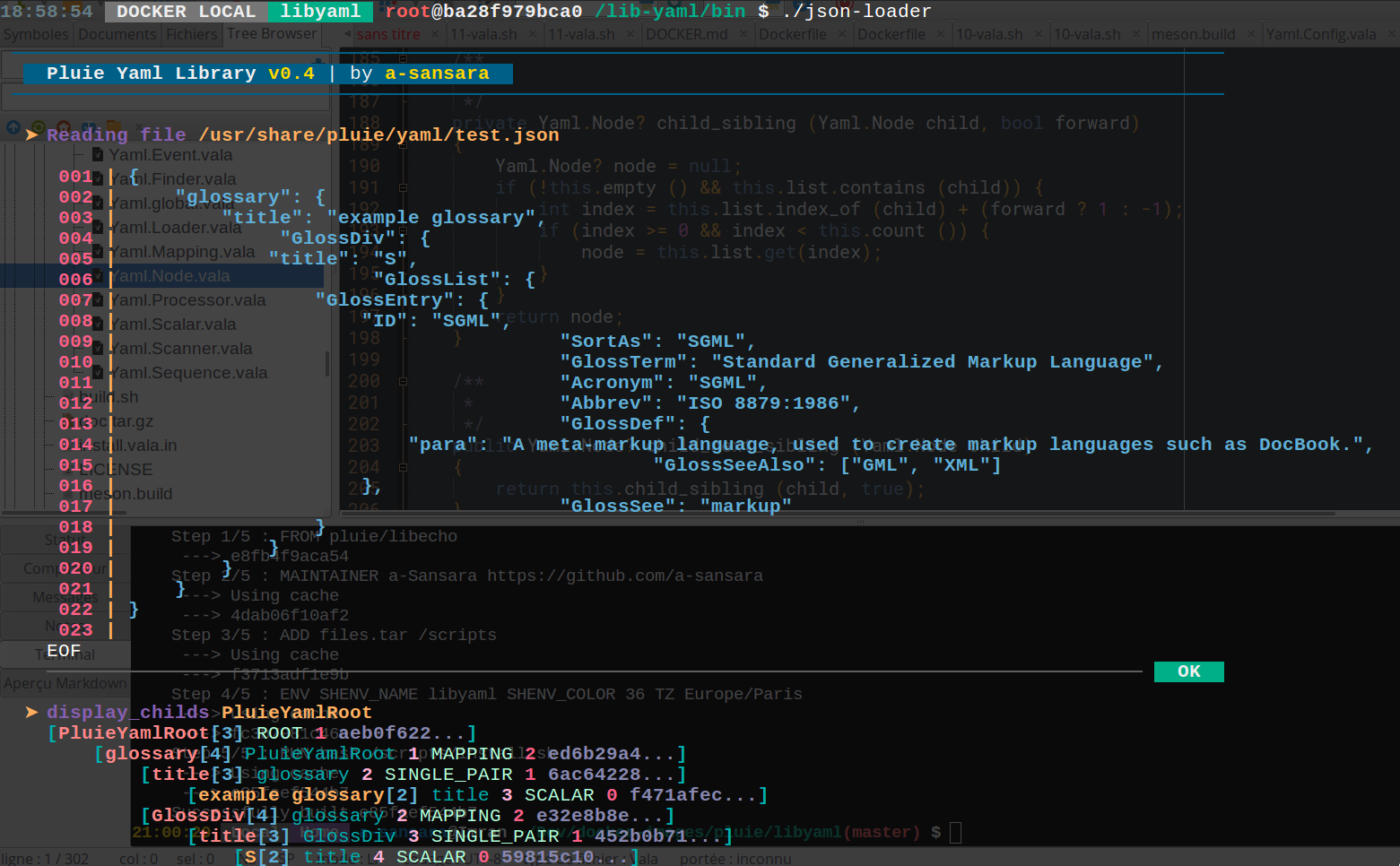
Docker
A demo image is now available on docker hub. To run a container :
docker run --rm -it pluie/libyaml
Then you can execute any samples, for example :
./json-loader
Usage
config
var config = new Yaml.Config (path);
var node = config.get ("ship-to.address.city{0}");
if (node != null) {
of.echo (node.data)
}
see Finder below to get precisions about config.get parameter (search path definition)
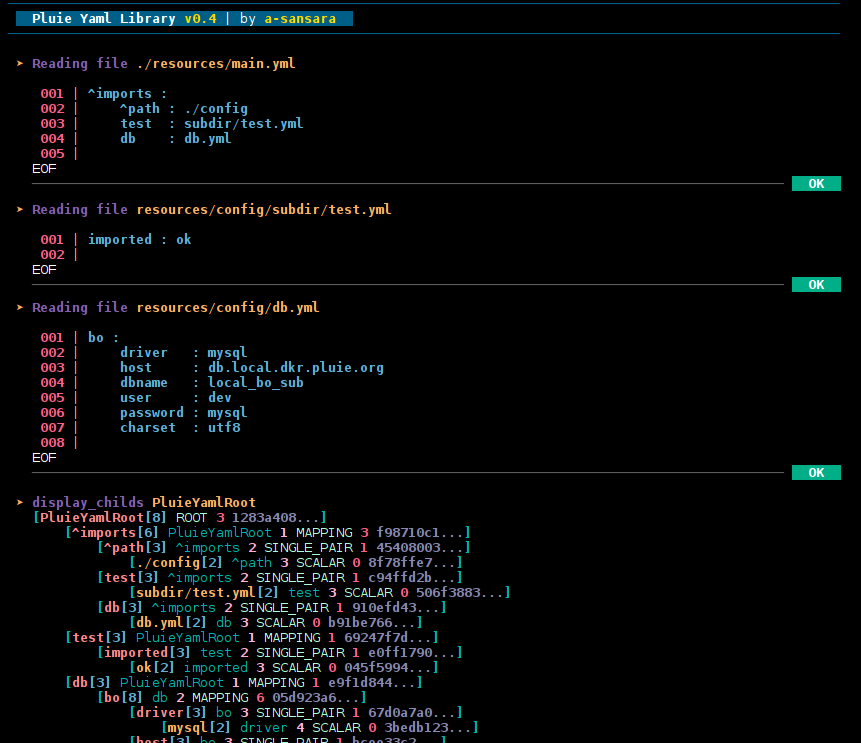
config with ^imports clause
# | use special key word '^imports' to import other yaml config files in
# | current yaml document
# | '^imports' must be uniq and a direct child of root node
# | imported files are injected as mapping nodes at top document level
# | so you cannot use keys that already exists in the document
^imports :
# you can redefine default import path with the special key '^path'
# if you do not use it, the default path value will be the current directory
# redefined path values are relative to the current directory (if a relative path
# is provided)
^path : ./config
# you can also define any other var by prefixing key with ^
^dir : subdir
# and use it enclosed by ^
# here final test path will be "./config/subdir/test.yml"
test : ^dir^/test.yml
# here final db path will be "./config/db.yml"
db : db.yml
legend display_childs :
[ node.name [refCount] node.parent.name node.level node.ntype.infos () node.count () node.uuid node.tag]
You can easily manage display tracing of yaml nodes by setting these var according to your needs :
using Pluie
...
// general debug display usefull informations
Yaml.DEBUG = false;
// drive display_childs method :
Yaml.DBG_SHOW_INDENT = true;
Yaml.DBG_SHOW_PARENT = false;
Yaml.DBG_SHOW_UUID = true;
Yaml.DBG_SHOW_LEVEL = false;
Yaml.DBG_SHOW_REF = false;
Yaml.DBG_SHOW_COUNT = true;
Yaml.DBG_SHOW_TAG = true;
Yaml.DBG_SHOW_TYPE = true;
...
loader
load a single document.
^imports clause is out of effects here.
var path = "./config/main.yml";
// uncomment to enable debug
// Pluie.Yaml.DEBUG = true;
var loader = new Yaml.Loader (path /* , displayFile, displayNode */);
if ((done = loader.done)) {
Yaml.Node root = loader.get_nodes ();
root.display_childs ();
}
finder
pluie-yaml provide a Yaml.Finder to easily retriew a particular yaml node.
Search path definition has two mode.
The default mode is Yaml.FIND_MODE.DOT
- child mapping node are separated by dot
- sequence entry must be enclosed in curly brace
ex : grandfather.father.son{2}.age
The Other mode is Yaml.FIND_MODE.SQUARE_BRACKETS
- node's key name must be enclosed in square brackets
- sequence entry must be enclosed in curly brace
ex : [grandfather][father][son]{2}[age]
with singlepair node, you can retriew corresponding scalar node with {0}
ex yaml file :
product:
- sku : BL394D
quantity : 4
description : Basketball
vala code :
...
var loader = new Yaml.Loader (path, true);
if ((done = loader.done)) {
Yaml.Node root = loader.get_nodes ();
var finder = new Yaml.Finder(root);
Yaml.Node? node = null;
if ((node = finder.find ("product{0}.description")) != null) {
var val = node.val ();
}
...
}
Traversing
via iterator
var config = new Yaml.Config (path);
var root = config.root_node ();
if (root != null && !root.empty ()) {
foreach (var child in root) {
// do stuff
of.echo (child.to_string ());
}
}
or
var config = new Yaml.Config (path);
var root = config.root_node ();
if (root != null && root.count () > 0) {
Iterator<Yaml.Node> it = root.iterator ();
Yaml.Node? child = null;
for (var has_next = it.next (); has_next; has_next = it.next ()) {
child = it.get ();
// do stuff
of.echo (child.to_string ());
}
}
other
if (!node.empty ()) {
Yaml.Node child = node.first();
of.action("loop throught mapping next sibling", child.name);
while (child!=null && !child.is_last()) {
// do stuff
of.echo (child.to_string ());
child = child.next_sibling ();
}
}
if (node.count () > 0) {
child = node.last();
of.action("loop throught mapping previous sibling", child.name);
while (child!=null && !child.is_first()) {
// do stuff
of.echo (child.to_string ());
child = child.previous_sibling ();
}
}
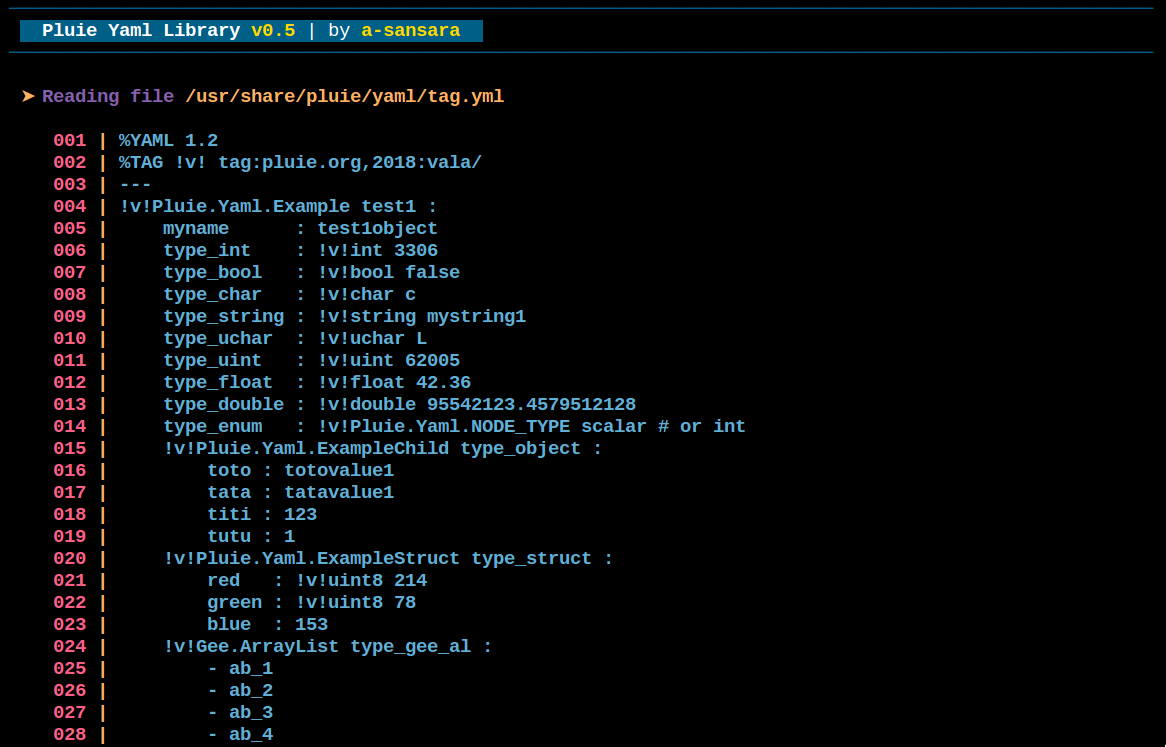
Tag Directives & Tag values
an example is available with samples/yaml-tag.vala sample
and resources/tag.yml file
on yaml side, proceed like that :
%YAML 1.2
%TAG !v! tag:pluie.org,2018:vala/
---
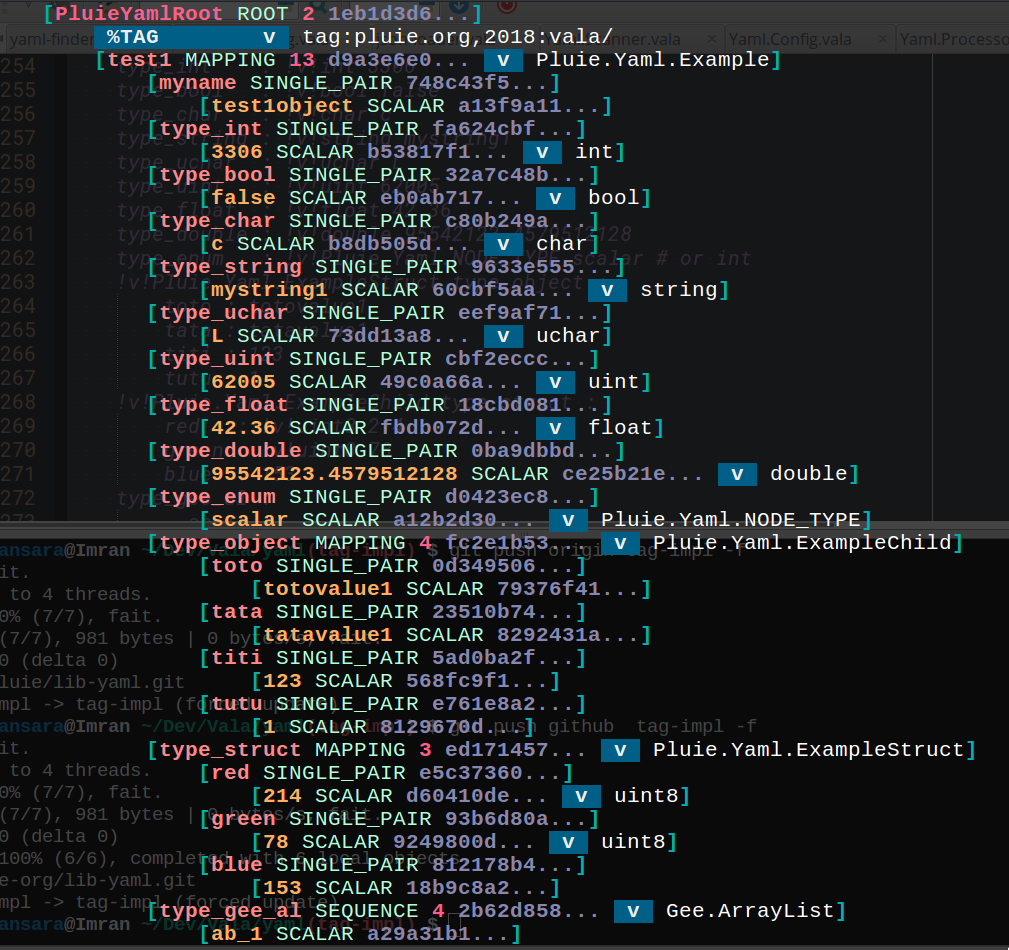
!v!Pluie.Yaml.Example test1 :
myname : test1object
type_int : !v!int 3306
type_bool : !v!bool false
type_char : !v!char c
type_string : !v!string mystring1
type_uchar : !v!uchar L
type_uint : !v!uint 62005
type_float : !v!float 42.36
type_double : !v!double 95542123.4579512128
type_enum : !v!Pluie.Yaml.NODE_TYPE scalar # or int
!v!Pluie.Yaml.ExampleChild type_object :
toto : totovalue1
tata : tatavalue1
titi : 123
tutu : 1
!v!Pluie.Yaml.ExampleStruct type_struct :
red : !v!uint8 214
green : !v!uint8 78
blue : 153
!v!Gee.ArrayList type_gee_al :
- ab_1
- ab_2
- ab_3
- ab_4
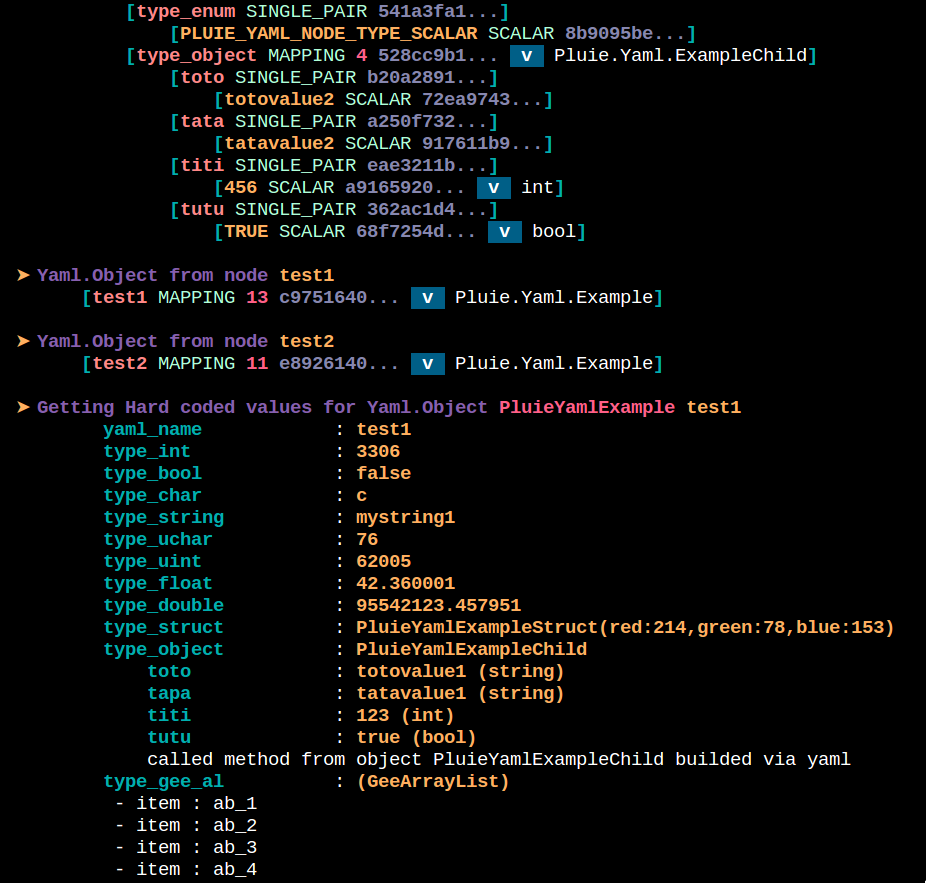
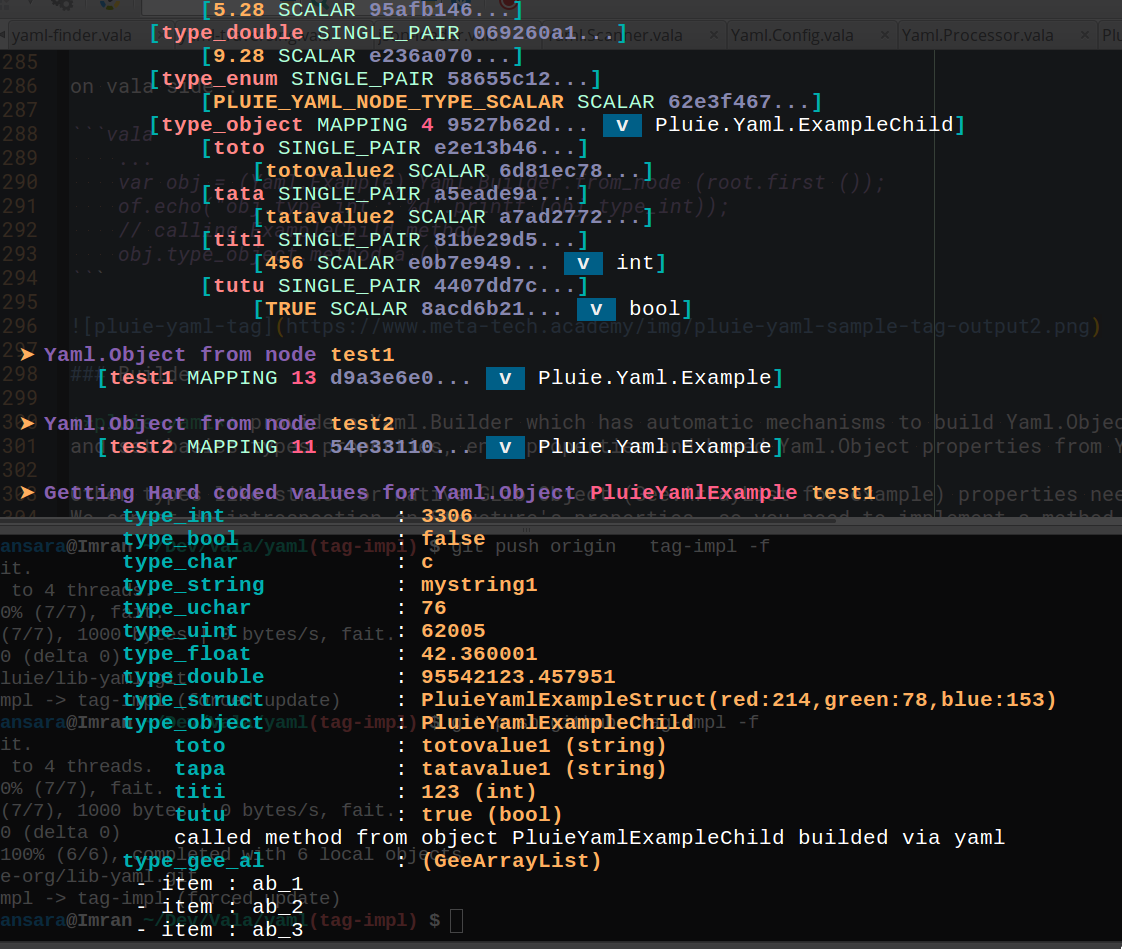
note : only the first level of yaml node matching a vala object need a tag. pluie-yaml has mechanisms to retriew properties types of a Yaml.Object. So basic vala types tag, enum tag, struct tag and derived Yaml.Object (here ExampleChild) or GLib.Object vala tags are not necessary inside a Yaml.Object.
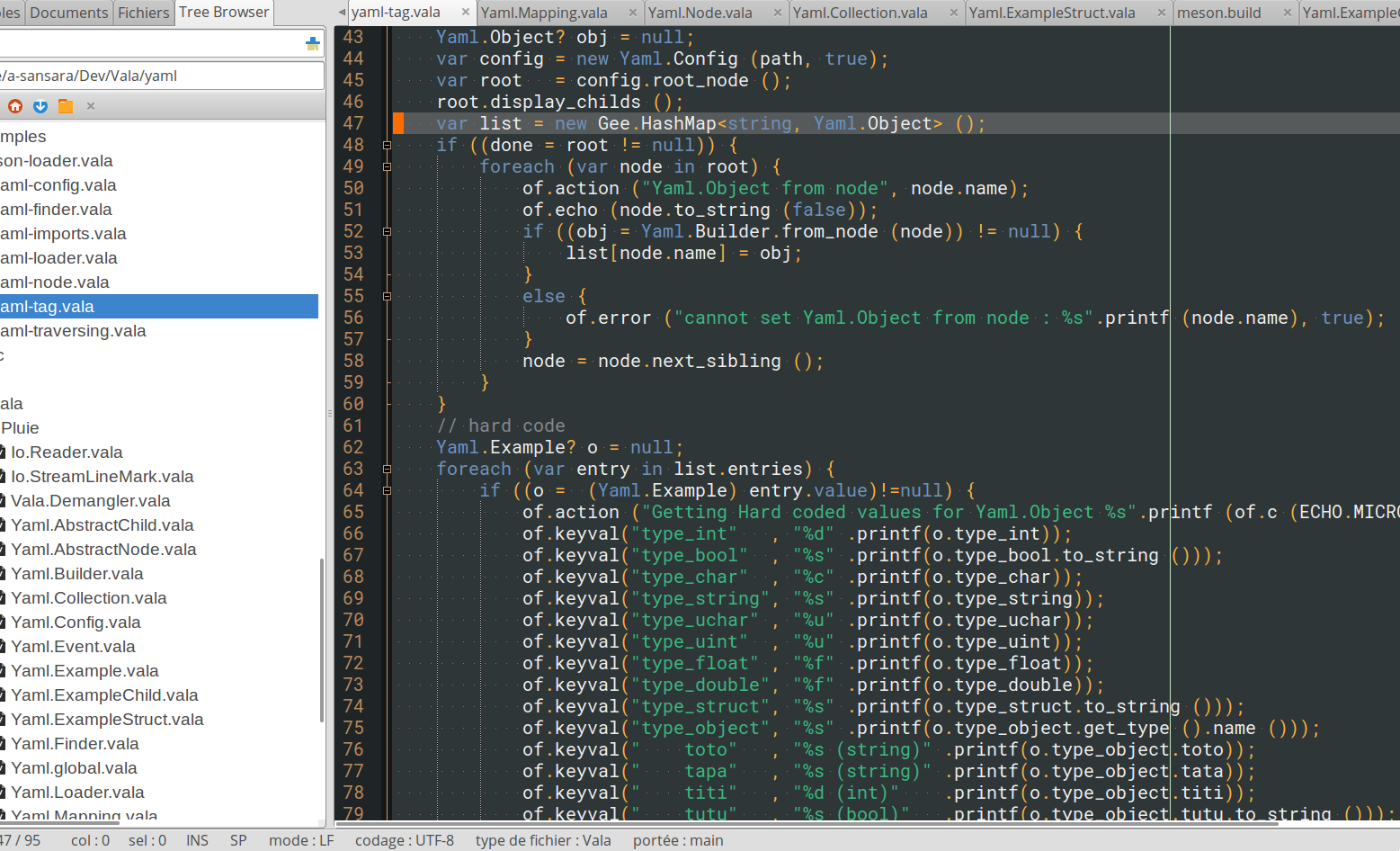
on vala side :
...
var obj = (Yaml.Example) Yaml.Builder.from_node (root.first ());
of.echo("obj.type_int : %d".printf (obj.type_int));
// calling ExampleChild method
obj.type_object.method_a ()
Builder
pluie-yaml provide a Yaml.Builder which has automatic mechanisms to build Yaml.Object instances (and derived classes) and set basics types properties, enum properties and based Yaml.Object properties from Yaml.node.
Other types like struct or native GLib.Object (Gee.ArrayList for example) properties need some stuff in order to be populated appropriately
We cannot do introspection on Structure's properties, so you need to implement a method which will do the job.
First at all, in the static construct of your class, you need to register (properties) types that need some glue for instanciation.
public class Example : Yaml.Object
{
static construct
{
Yaml.Object.register.add_type (
typeof (Yaml.Example), // owned type
typeof (Yaml.ExampleStruct), // property type
typeof (Gee.ArrayList) // property type
);
}
...
Secondly you must override the public void populate_from_node (Glib.Type, Yaml.Node node) Yaml.Object original method.
populate_from_node is automatically called by the Yaml.Builder if the type property is prealably registered.
Example of implementation from src/vala/Pluie/Yaml.Example.vala :
public override void populate_from_node(GLib.Type type, Yaml.Node node)
{
if (type == typeof (Yaml.ExampleStruct)) {
this.type_struct = ExampleStruct.from_yaml_node (node);
}
else if (type == typeof (Gee.ArrayList)) {
this.type_gee_al = new Gee.ArrayList<string> ();
if (!node.empty ()) {
foreach (var child in node) {
this.type_gee_al.add(child.data);
}
}
}
}
Once your class has this glue, you can deal with complex object and populate them directly from yaml files.
for more details see :
src/vala/Pluie/Yaml.Example.valasrc/vala/Pluie/Yaml.ExampleChild.valasrc/vala/Pluie/Yaml.ExampleStruct.valasamples/yaml-tag.vala
code from samples/yaml-tag.vala :
output from samples/yaml-tag.vala :
Build Yaml.Node from Yaml.Object
reverse build mechanism is also possible but have the same limitation.
you need to override the public Yaml.Node? populate_to_node(GLib.Type type, string name) Yaml.Object original method
populate_to_node is also automatically called by the Yaml.Builder if the type property is prealably registered.
Example of implementation from src/vala/Pluie/Yaml.Example.vala :
public override Yaml.Node? populate_to_node(GLib.Type type, string name)
{
Yaml.Node? node = base.populate_to_node (type, name);
// non Yaml.Object type & registered type
if (node == null) {
if (type == typeof (Yaml.ExampleStruct)) {
node = new Yaml.Mapping (null, name);
new Yaml.Mapping.with_scalar (node, "red" , this.type_struct.red.to_string ());
new Yaml.Mapping.with_scalar (node, "green", this.type_struct.green.to_string ());
new Yaml.Mapping.with_scalar (node, "blue" , this.type_struct.blue.to_string ());
}
else if (type == typeof (Gee.ArrayList)) {
node = new Yaml.Sequence (null, name);
foreach (var data in this.type_gee_al) {
new Yaml.Scalar (node, data);
}
}
}
return node;
}
for more details see :
samples/yaml-tonode.vala
more samples
see samples files in ./samples directory
todo
imports clausefix nodes traversingrewrite nodes classesput doc onlineadd docker image- manage tag directives & tag (partially done)
- improve doc
- dumper